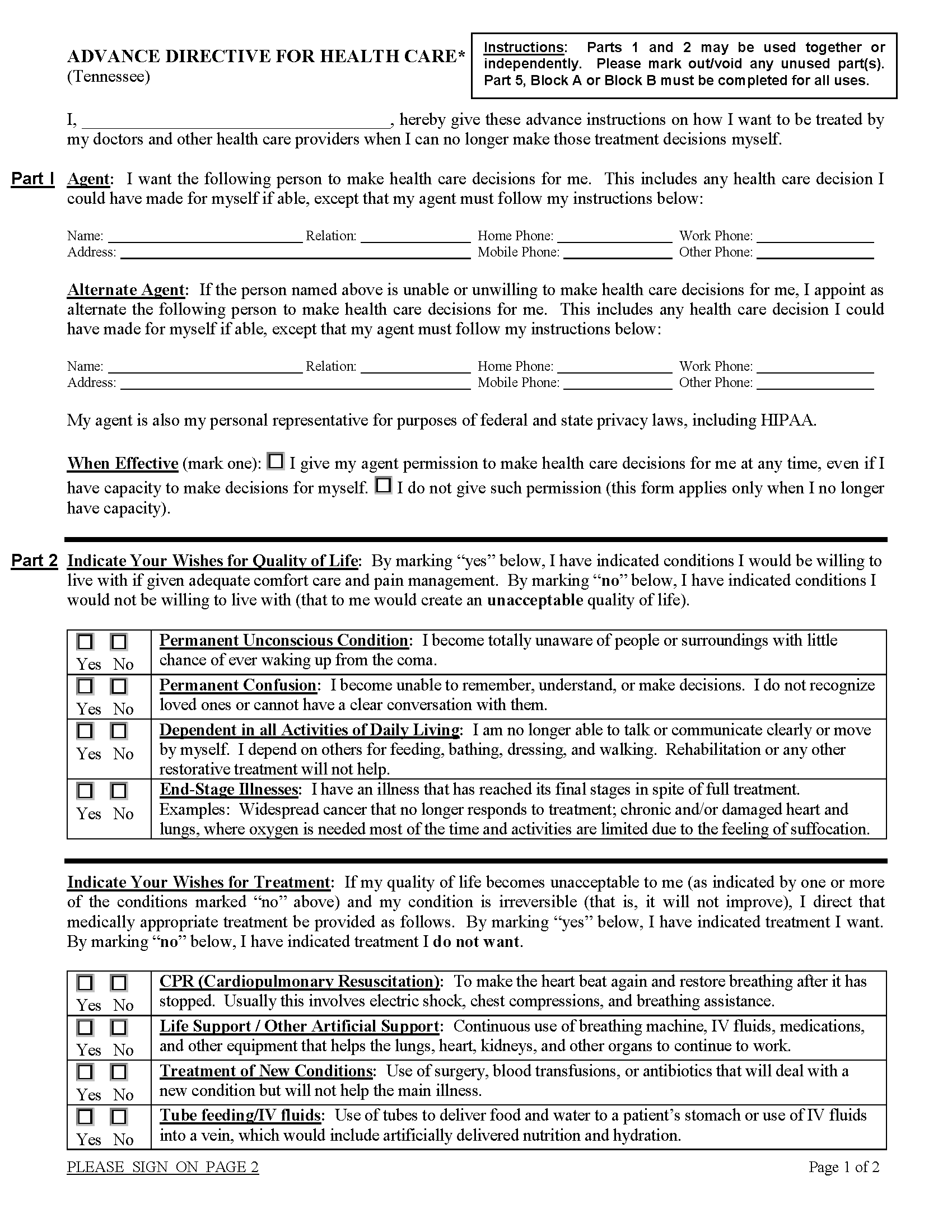
Signing Requirements
Advance directives must be notarized or signed by two witnesses over 18.[1]
The witnesses cannot be the principal’s agent, and at least one cannot be:
- Related by blood, marriage, or adoption; or
- Entitled to the principal’s estate.
Advance Directive (Preview)
Revocation
The following actions revoke an agent’s authority:
- A principal with capacity executing a written statement of revocation
- A principal with capacity personally notifying their healthcare provider
- Decrees of annulment, divorce, or separation (if the spouse is the agent)