By Type (4)
 General Warranty Deed – Provides a warranty that there are no defects on the title and that the grantor has the right to transfer. General Warranty Deed – Provides a warranty that there are no defects on the title and that the grantor has the right to transfer.
|
 Quit Claim Deed – A conveyance instrument that doesn’t include any warranty regarding the property title’s quality. Quit Claim Deed – A conveyance instrument that doesn’t include any warranty regarding the property title’s quality.
|
 Special Warranty Deed – Promises that no claims or encumbrances resulted from the grantor’s ownership. Special Warranty Deed – Promises that no claims or encumbrances resulted from the grantor’s ownership.
|
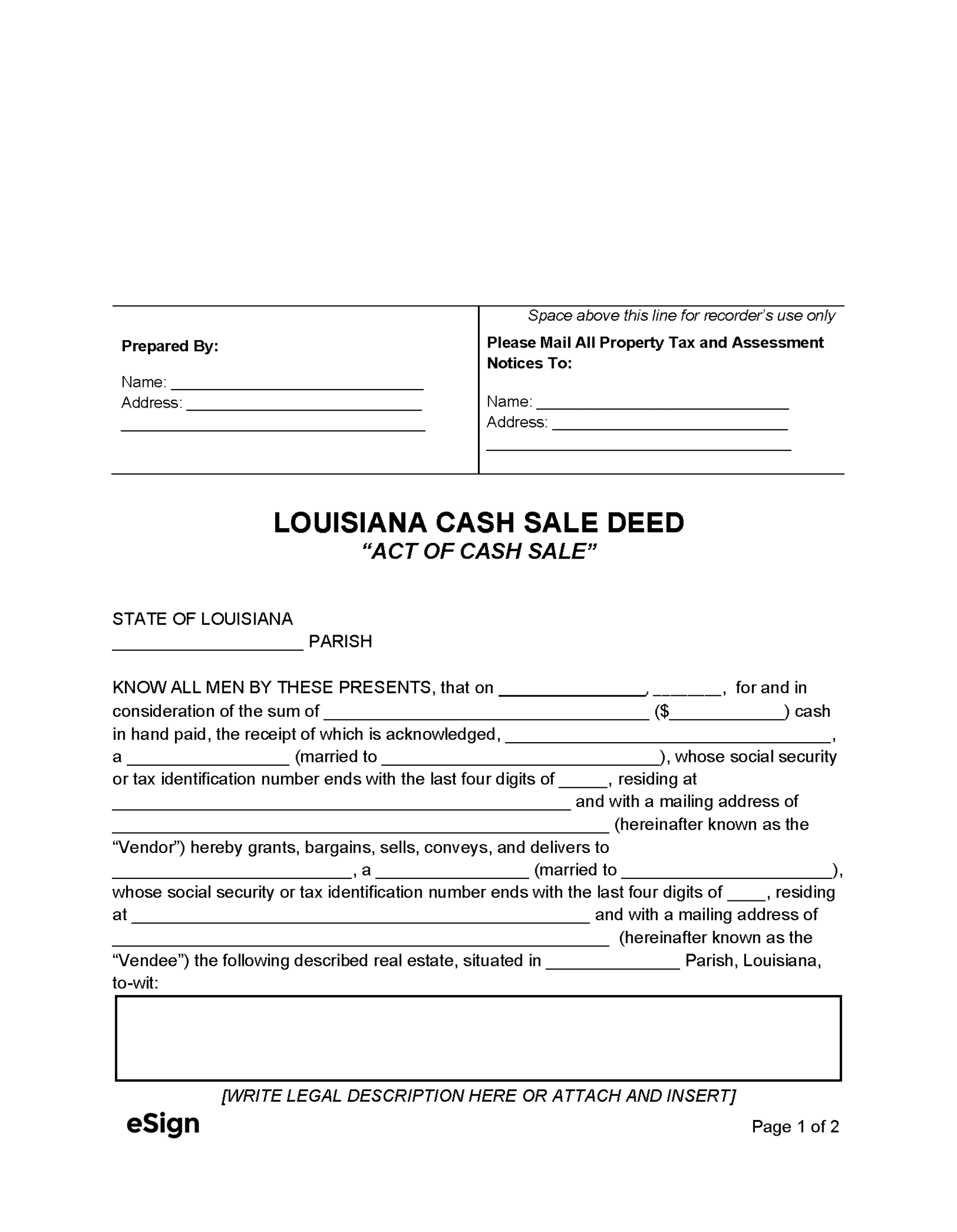 Cash Sale Deed – Used when the buyer pays in cash. Cash Sale Deed – Used when the buyer pays in cash.
|
Formatting
Paper – 8.5″ x 11″ or 8.5″ x 14″
Margins – 2″ top margin on first page, all other margins 1″
Font – At least 8pt[1]
Recording
Signing Requirements – Deeds must be signed by the grantor, a notary public, and two witnesses.[2]
Where to Record – Deeds are filed with the local Clerk of Court’s Office.[3]
Cost – $100, $200 if more than 5 pages (as of this writing)[4]
